
In India’s fast-growing digital economy, speed, reliability, and uptime are not just nice-to-haves; they’re business-critical. Whether you run an e-commerce platform, a SaaS firm, a financial services company, or a high-traffic web portal — the data center you choose can make or break your user experience and reputation. Two of the most talked-about options are Tier 3 and Tier 4 colocation or data-center facilities.
In this blog post, we’ll compare them in the context of the Indian market (especially cities like Mumbai or Delhi), and highlight why a service like the one from ESDS provide just the right balance between reliability and cost for many businesses.
Understanding Data Center Tiers: What They Mean
The concept of “data center tiers” comes from Uptime Institute — a globally recognized body that evaluates data-center infrastructure. The tiers (from 1 to 4) reflect increasing levels of redundancy, fault tolerance, and uptime guarantees.
Here’s an overview:
- Tier 1: Basic facility — single path for power/cooling, no redundancy. Uptime 99.671%.
- Tier 2: Some redundancy (partial N+1), but still limited. Uptime 99.741%.
- Tier 3: Fully redundant paths for power and cooling, N+1 redundancy for components, and capability for concurrent maintenance. Uptime 99.982%. Downtime limited to 1.6 hours per year.
- Tier 4: Fault-tolerant facility with 2N or 2N+1 redundancy (i.e. every critical component is duplicated), physically isolated systems, fully independent distribution paths — meaning even during maintenance or component failure, services run uninterrupted. Uptime 99.995%, downtime under 26 minutes per year.
Because each tier builds upon the previous, a Tier 4 data center inherently meets all the requirements of Tier 3 — and then some.
Nevertheless, a higher tier doesn’t always automatically translate to “better fit” — it depends on your actual business needs and risk profile.
Who Should Use Tier 3 and Who Needs Tier 4?
When Tier 3 is important
Tier 3 is often the sweet spot for many businesses — especially in India — because it offers significant reliability without the huge cost overhead of a Tier 4 facility. Typical use cases:
- Companies handling non-mission critical workloads, internal applications, standard hosting, backups, dev/staging environments.
- SMEs / mid-size firms that need high availability, but don’t have 24×7-global-traffic or extremely stringent uptime requirements.
- Businesses looking for colocation with good redundancy for growth, but want to avoid overpaying for infrastructure they don’t fully need.
With an expected downtime of just 1.6 hours per year, a Tier 3 data center offers “good enough” reliability for a large number of business applications, while keeping costs relatively reasonable.
When Tier 4 becomes essential
Tier 4 makes sense when downtime is absolutely unacceptable, or when your infrastructure has to support heavy, continuous traffic, strict SLAs, or mission-critical workloads. Examples:
- Financial services, banking, fintech — where every minute of downtime can cost money, compliance, or reputation.
- Large-scale e-commerce / online marketplaces with high traffic volumes and peak loads.
- Real-time services or SaaS platforms used globally, including 24×7 operations.
- Enterprises with compliance / regulatory requirements and risk-averse clients who demand “always on” availability.
With downtime reduced to less than 26 minutes a year — even during maintenance — Tier 4 data centers provide the highest-level fault tolerance and availability.
Tier 3 /Tier 4 Colocation Facilities: What Works for Indian Businesses
While global standards define what “Tier 3” or “Tier 4” means, on-the-ground reality and pricing differ widely, especially in India.
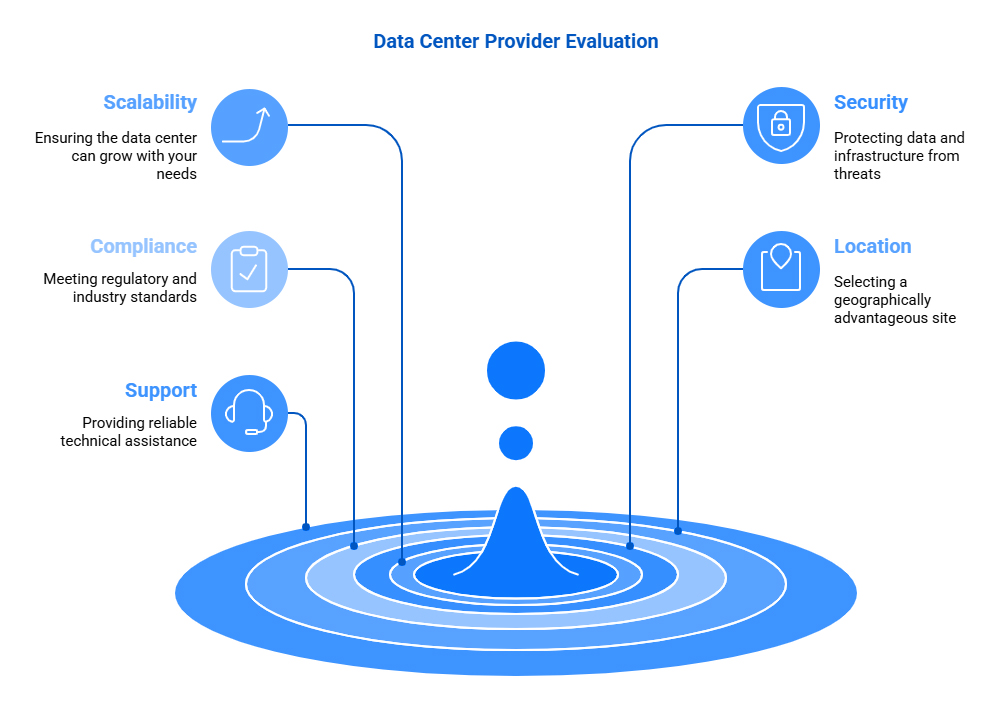
- In major metros such as Mumbai or Delhi — where latency, data-proximity, regulatory compliance, and connectivity matter — picking the right tier becomes more strategic than just technical.
- Many Indian businesses don’t actually need the “absolute uptime bullet-proofing” that Tier 4 offers — but they still want stability, security, and professional-grade infrastructure.
- Colocation providers in India, including those offering Tier 3 facilities, now come with robust redundancy, modern cooling, backup power, and managed services — making them a solid fit for many firms.
This is where a colocation provider like ESDS becomes relevant.
ESDS: The Right Partner for Your Business Need
ESDS offers colocation services through its network of Tier III-certified data centers located across India — Nashik, Navi Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Mohali.
Here’s why many businesses, especially in Mumbai, Delhi NCR, or other metro clusters, consider ESDS:
- Purpose-built Tier III data centers — designed for redundancy (power, cooling), high-availability infrastructure, and professional-grade security.
- Managed colocation & flexibility — ESDS provides not only rack space, power, and cooling, but also managed services like backup, monitoring, network management — freeing businesses from the hassle of maintaining physical infrastructure.
- Scalable & geographically distributed footprint — with multiple data centers across India, ESDS enables enterprises to co-locate servers near their user bases (e.g. Mumbai or Delhi), improving latency and compliance.
- Cost-conscious reliability — For many growing businesses, ESDS’s Tier III colocation offers a reliable, enterprise-grade infrastructure without the premium of a full Tier 4 facility — making it a pragmatic, business-friendly choice.
Tier 3 vs Tier 4 : A Comparison for Indian Businesses
| Factor | Tier 3 | Tier 4 |
| Uptime guarantee | 99.982% | 99.995% |
| Redundancy / Fault Tolerance | N+1 redundant power/cooling paths; can perform maintenance without downtime. | 2N or 2N+1 full redundancy; dual independent systems ensuring fault tolerance even during failures. |
| Typical Use Cases | Large SMEs, high-traffic sites with moderate tolerance for maintenance downtime, internal hosting, backup, colocation. | Critical services — finance, large-scale SaaS, e-commerce, high-availability global platforms. |
| Cost | Lower compared to Tier 4 — good cost-to-performance ratio. | Higher — because of more redundancy, infrastructure, maintenance complexity. |
How to Decide: Which Tier Is Right for Your Business?
Here are the questions you should ask when choosing between Tier 3 and Tier 4:-
- How critical is uptime for your business?
- If even a few hours of downtime per year could mean huge revenue loss, compliance failure or reputational damage — Tier 4 merits consideration.
- If your business can tolerate occasional maintenance windows or minimal downtime — Tier 3 often offers the best balance.
- What’s your budget vs. value proposition?
- Tier 4 involves higher capital expenditure (or recurring costs, in colocation). If your ROI from that extra uptime doesn’t justify the cost — Tier 3 makes financial sense.
- For budget-conscious firms wanting enterprise-grade reliability, colocation with a provider like ESDS gives you infrastructure you probably wouldn’t want to invest in building from scratch.
- What’s the nature of your workloads?
- Are you running mission-critical applications, financial transactions, real-time services, e-commerce or regulated workloads (healthcare, payments)? If yes — Tier 4 or equivalent redundancy is wise.
- If you host websites, internal databases, backups, dev/staging environments, or moderately trafficked services — Tier 3 is typically sufficient.
- Do you need geographical presence in specific metros (Mumbai, Delhi, etc.)?
- If you want to keep data closer to your end-users for latency or compliance, or if you want distributed presence — look for a colocation provider with multiple data centers across India (like ESDS).
- You may get better latency, redundancy, and cost-effectiveness than rolling out your own data centers.
- What about flexibility and scalability?
- Colocation providers often let you scale up/down — ideal for businesses growing in phases.
- Building or leasing a Tier 4 facility may involve high CAPEX and long-term commitment, which may not align with growth plans.
For many Indian companies — mid-size firms, high-traffic websites, SaaS platforms, local e-commerce players, and growing businesses — a Tier 3 colocation solution from a reliable provider like ESDS offers a great balance of reliability, affordability, and scalability.
On the other hand, if you operate a business where every second of downtime matters (e.g. payment processing, online trading, global-scale SaaS, real-time services), then you should strongly consider Tier 4 — or a distributed “multi-zone” architecture using multiple Tier 3 data centers to achieve redundancy at a lower overall cost.
For many businesses in Mumbai, Delhi, or other Indian metros, Tier 3 + colocation offers optimal cost-to-performance-value, while the “upgrade” to Tier 4 makes sense only when your risk and cost of downtime dramatically outweighs infrastructure cost.
Final Thoughts
Choosing a data center tier isn’t just a technical decision — it’s a strategic one. While Tier 4 represents the pinnacle of redundancy and uptime, it also comes with significantly higher cost and complexity. Many businesses — especially in India — will find that a well-run Tier 3 colocation facility delivers more than enough reliability, redundancy, and scalability to meet their needs.
If you want a data-center partner that understands the Indian market, offers robust colocation in Mumbai, Nashik, Bengaluru and beyond, and balances cost with reliability — ESDS is definitely worth evaluating.
That said, every business is unique. The “right fit” depends on your uptime tolerance, workload criticality, budget, and growth plans. Use this guide as a starting point — and do a detailed evaluation of your own business needs before committing.













Recent Comments